Briefly Describe the Brain Changes That Occur in Adolescence
In rodents and primates this pathway undergoes extensive changes during adolescence. Puberty is the process of sexual maturation that often signals the beginning of adolescence.
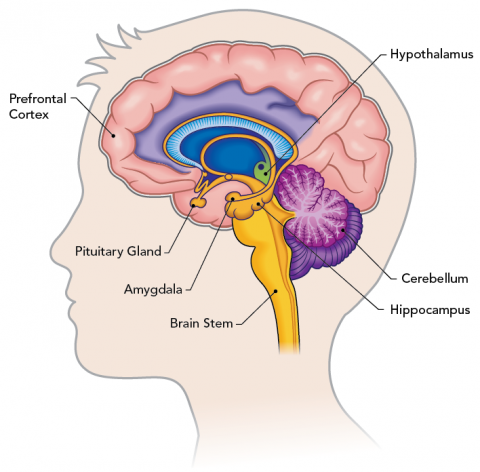
Understanding The Teen Brain Let S Talk Science
3 GIRLS brains are SMALLER but reach their maximum volume EARLIER.

. Briefly describe the brain changes that occur in adolescence. Adolescence begins at puberty which now occurs earlier on average than in the past. He says that development of the executive functions along with other changes during the teen years combine to create important modifications in how the brain functions during adulthood.
One of the most striking changes is the steady linear increase in dopaminergic neural projections that happens in both males and females in the brain area known as the medial prefrontal cortex or mPFC. 2 brain morphology is tied to HEREDITY more than environmental factors. It includes some big changesto the body and to the way a young person relates to the world.
In adolescence this part of the brain thickens to improve information processing. Children who are entering adolescence are going through many changes physical intellectual personality and social developmental. In adolescence changes in the brain interact with experience knowledge and social demands and produce rapid cognitive growth.
Briefly describe the brain changes that occur in adolescence. The body is transformed from a childs body into an adults body with dramatic changes in size appearance and function. The three most important structural changes in the brain that occur during adolescence takes place in the Corpus Callosum Prefrontal Cortex and the Limbic System.
Adolescence is the period of transition between childhood and adulthood. People often deride the function of the frontal cortex in teenagers. In the US the average age of onset of puberty is for girls ages 1011 years and for boys ages 1112.
Rewarding things feel more rewarding explains Steinberg. A shifts in activity from the limbic system to the prefrontal cortex b an increase in myelination of the frontal cortex c remodeling pruning of synaptic connection and. USE IT OR LOSE IT.
Increases efficiency improves memory IQ and READING not in PFC Interesting facts. During adolescence myelination and synaptic pruning in the. They are characterised by the development of higher-level cognitive functioning that aligns with the changes in brain structure and function particularly in the prefrontal cortex region.
Some of the most developmentally significant changes in the brain occur in the prefrontal cortex which is involved in decision making and cognitive control as well as other higher cognitive functions. Shifts in activity from the limbic system to the prefrontal cortex b an increase in myelination of the frontal cortex c remodeling pruning of synaptic connection and d an overall decrease in metabolism. Many synapses are eliminated while at the same time there is an increase in white matter 9 10 and there are changes in neurotransmitter systems as well 11 e1 e2.
We believe that these changes adjust and tune the brain in order to sculpt learning and decision-making at these different life stages. Large-scale longitudinal studies have shown that a basic reorganization of the brain occurs during adolescence. The physical changes of the brain that occur during adolescence follow typical patterns of cognitive development.
Thus the anatomical and physiological maturation processes that take place in. The Corpus Callosum is a bundle of axon fibers that connects the left and right hemispheres together. There are dramatic changes in neural circuits particularly in frontal cortical and basal ganglia circuits during adolescence.
During adolescence brain cells continue to bloom in the frontal region. This stage of cognitive development termed by Piaget as the formal operational stage marks. These qualities would help the teenager make sounder decisions in a responsible job like that of babysitting young children.
With the maturation of the prefrontal cortex teenagers think with greater maturity responsibility and intelligence than ten or eleven year olds. During adolescence there are changes involving the way the brain processes rewards and pleasure. The end of adolescence is tied to social and.
The growth of the brain during adolescence is caused by a rapid increase in the total number of neurons. Adolescence is the period of transition between childhood and adulthood. Second the adolescent brain may be more responsive to the glucocorticoids than the adult brain as a previous animal study indicated that an equivalent dose of corticosterone increased gene expression to a greater degree in the adolescent compared to adult hippocampus Lee Brandy Koenig 2003.
Finally due to the increases in hormonal stress reactivity described above it. 1 Brain volume DECREASES during adolescence. Adolescence is a particularly dynamic period of brain development second only to infancy in the extent and significance of the neural changes that occur.
Brain Changes during Adolescence. During adolescence myelination and synaptic pruning in the prefrontal cortex increase s improving the efficiency of information processing and neural connections between the prefrontal cortex and other regions of the brain are strengthened. The growth of the brain during adolescence is caused by a rapid increase in the total number of neurons.
The purpose of this review is to describe the changes that occur in HPA function during adolescence as well as briefly discuss the possible ramifications of these changes on the developing brain and psychological health. The nature of these changesin brain structures functions and connectivityallows for a remarkable amount of developmental plasticity unique to this period of life making adolescents amenable to change. The changes in how adolescents think reason and understand can be even more dramatic than their obvious physical changes.
Briefly describe the brain changes that occur in adolescence. However this growth takes time and the growth is uneven. The many physical sexual cognitive social and emotional changes that happen during this time can bring anticipation and anxiety for both children and their families.
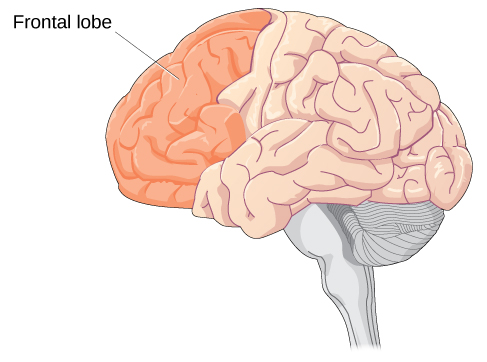
Brain Development During Adolescence Lifespan Development
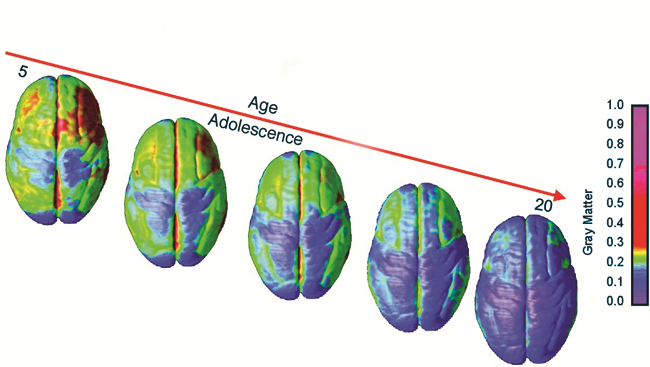
0 Response to "Briefly Describe the Brain Changes That Occur in Adolescence"
Post a Comment